Data Integration Importance
By
On most every CIO’s key objectives is to integrate their organization’s data. In fact the issue of data integration has risen all the way to the CFO and CEO level of a corporation. A key question is why is data integration becoming so important to so many C-level executives? There are several key reasons driving this desire:
-
Provide IT Portfolio Management
-
Reduce IT Redundancy
-
Prevent IT Applications Failure
Provide IT Portfolio Management
Over the years I have had the opportunity to perform over a dozen data warehousing assessments. During these assessments I always ask the client how much they spend annually on data warehousing. The majority of companies and government organizations cannot give a relatively good estimate on what they actually spend. In order to manage these and any other costly information technology (IT) initiatives it is critical to measure each one of them. However, it is impossible to measure them when most companies do not understand them (see Figure 1: “How To Manage IT”). This is where IT Portfolio Management enters the picture.
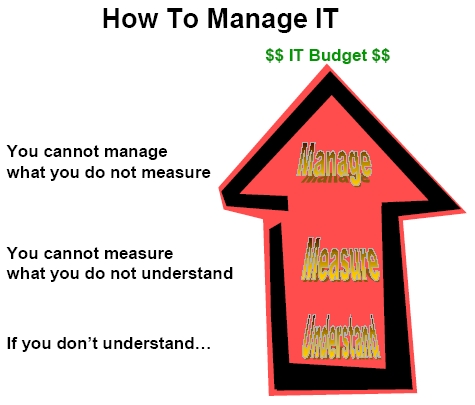
Figure 1: How To Manage IT
IT portfolio management refers to the formal process for managing IT assets. An IT asset is software, hardware, middleware, IT projects, internal staff, applications and external consulting. Like every newer discipline, many companies that have started their IT ortfolio management efforts have not done so correctly. I would like to list out some of the keys to building successful IT portfolio management applications.
By properly managing their IT portfolio it allows the corporation to see which projects are proceeding well and which are lagging behind. In my experience, almost every large company has a great deal of duplicate IT effort occurring (see later section on “Reduce IT Redundancy”).
This happens because the meta data is not accessible. At my company we have a couple of large clients whose primary goal is to remove these tremendous redundancies, which translates into tremendous initial and ongoing IT costs.
Reduce IT Redundancy
CIO is commonly defined as Chief Information Officer; however, there is another possible meaning to this acronym; Career Is Over. One of the chief reasons for this is that most IT departments are “handcuffed” in needless IT redundancy that too few CIOs are willing and capable of fixing.
There are several CIO surveys that are conducted annually. These surveys ask “what are your top concerns for the upcoming year”. Regardless of the survey you look at “data integration” will be high on the list. Now data integration has two facets to it. One is the integration of data across disparate systems for enterprise applications. The second is the integration/removal of IT redundancies. Please understand that some IT redundancy is a good thing. For example, when there is a power outage and one of your data centers is nonoperational you need to have a backup of these systems/data. However, when I talk about IT redundancies I am addressing “needless” IT redundancy. Meaning, IT redundancy that only exists because of insufficient management of our IT systems. I was working with a Midwestern insurance company that, over a four year span had initiated various decision support efforts. After this four year period they took the time to map out the flow of data from their operational systems, to their data staging areas and finally to their data mart structures. What they discovered was Figure 2: “Typical IT Architecture”.
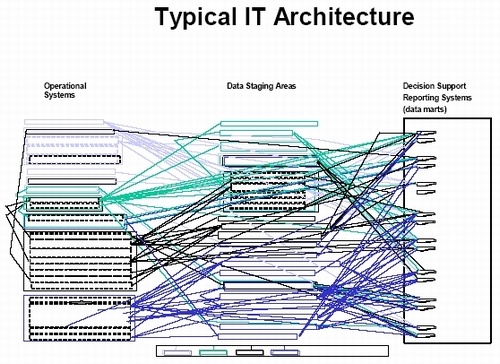
Figure 2: Typical IT Architecture
What is enlightening about Figure 2 is that when I show this illustration during a client meeting or at a conference keynote address the typical response that I receive from the people is “Where did you get a copy of our IT architecture?” If you work at a Global 2000 company or any large government entity, Figure 2 represents an overly simplified version of your IT architecture.
These poor architecture habits create a litany of problems including:
-
Needless IT ReworkRedundant Hardware/Software
-
Redundant Applications/Processes/Data
-
Needless IT Rework
-
Redundant Hardware/Software
Redundant Applications/Processes/Data
It has been my experience working with large government agencies and Global 2000 companies that needlessly duplicate data is running rampant throughout our industry. In my experience the typical large organization has anywhere between 3 – 4 fold needless data redundancy. Moreover, I can name multiple organizations that have literally hundreds of “independent” data mart applications spread all over the company. Each one of these data marts is duplicating the extraction, transformation and load (ETL) that is typically done centrally in a data warehouse. This greatly increases the number of support staff required to maintain the data warehousing system as these tasks are the largest and most costly data warehousing activities. Besides duplicating this process, each data mart will also copy the data as well requiring further IT resources. It is easy to see why IT budgets are straining under the weight of all of this needless redundancy.
Needless IT Rework
During the requirements gathering portion of one of our meta data management initiatives I had an IT project manager discuss the challenges that he is facing in analyzing one of the mission-critical legacy applications that will feed the data warehousing application that his team has been tasked to build. During our interview he stated, “This has to be the twentieth time that our organization is analyzing this system to understand the business rules around the data.”
This person’s story is an all too common one as almost all organizations reinvent the IT wheel on every project. This situation occurs because usually separate teams will typically build each of the IT systems and since they don’t have a Managed Meta Data Environment (MME), these teams do not leverage the other’s standards, processes, knowledge, and lessons learned. This results in a great deal of rework and reanalysis.
Redundant Hardware/Software
I have discussed a great deal about the redundant application and IT work that occurs in the industry. All of this redundancy also generates a great deal of needless hardware and software redundancy. This situation forces the enterprise to retain skilled employees to support each of these technologies. In addition, a great deal of financial savings is lost, as standardization on these tools doesn’t occur. Often a software, hardware, or tool contract can be negotiated to provide considerable discounts for enterprise licenses, which can be phased into. These economies of scale can provide tremendous cost savings to the organization. In addition, the hardware and software that is purchased is not used in an optimal fashion. For example, I have a client that has each one of their individual IT projects buy their own hardware. As a result, they are infamous for having a bunch of servers running at 25% capacity.
From the software perspective the problem only gets worse. While analyzing a client of mine I had asked their IT project leaders what software vendors have you standardized on? They answered “all of them!” This leads to the old joke “What is the most popular form of software on the market? Answer…Shelfware!” Shelfware is software that a company purchases and winds up never using and it just sits on the shelf collecting dust.
Prevent IT Applications Failure
When a corporation looks to undertake a major IT initiative, like a customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), data warehouse, or e-commerce solution their likelihood of project failure is between 65% – 80%, depending on the study referenced. This is especially alarming when we consider that these same initiatives traditionally have executive management support and cost many millions of dollars. For example, I have one large client that is looking to roll out a CRM system (e.g. Siebel, Oracle) and an ERP system (e.g. SAP, PeopleSoft) globally in the next four years. Their initial project budget is over $125 million!
In my opinion they have a 0% probability of delivering all of these systems on-time and onbudget. Consider this, when was that last time that you’ve seen an ERP or CRM initiative being delivered on time or on budget? When we examine the causes for these projects failure several themes become apparent. First, these projects did not address a definable and measurable business need. This is the number one reason for project failure, data warehouse, CRM, MME, or otherwise. As IT professionals we must always be looking to solve business problems or capture business opportunities. Second, the projects that fail have a very difficult time understanding their company’s existing IT environment and business rules. This includes custom applications, vendor applications, data elements, entities, data flows, data heritage and data lineage.
MME’s Focus On Data Integration
Many of these Global 2000 companies and large government organizations are targeting MME technology to assist them in identifying and removing existing application and data redundancy. Moreover, many companies are actively using their MME to identify redundant applications through analysis of the data. These same companies are starting IT application integration projects to merge these overlapping systems and to ensure that future IT applications do not proliferate needless redundancy.
If your organization can reduce their applications, processes, data, software and hardware, lowers the likelihood for IT project failure and speeds up the IT development life-cycle, then clearly it will greatly reduce a company’s IT expenditures. For example, I have a large banking client that asked my company to analyze their IT environment. During this analysis we discovered that they have a tremendous amount of application and data redundancy. Moreover, I had figured out that they have over 700 unique applications. I then compared this client to a bank that is more than twice there size; however, this larger bank has a world class MME and uses it to properly manage their systems. As a result, they have less than 250 unique applications. Clearly the bank with more than 700 applications has a great deal of needless redundancy as compared to a bank that is more than twice their size and has less than 250 applications. Interestingly enough the bank that has less than 250 applications and has a world-class MME is also 14 times more profitable than the bank maintaining over 700 applications. It doesn’t seem like a very far stretch to see that the less profitable bank would become much more profitable if they removed this redundancy.