Meta Data ROI: Specific Guidelines for Your Company
By David Marco
This article represents the third and concluding portion of my three part series on defining the return on investment (ROI) that a meta data repository can provide to your company. The formulas that I will present in this article are meant to be used as guidelines; the results that you experience on your project will differ.
Now that I’m finished with the legal disclaimer on to the calculations. In building these formulas I have attempted to err on the side of being overly conservative. There are several companies that are achieving more favorable ROI percentages than the ones that I will present. On the other hand, those companies that do not properly define their meta data objectives and do not correctly build their repositories attain much worse results. Before you start counting your profits there are two paradigm shifts that must occur. First, the key to attaining a positive ROI is that the people must act on the information that meta data provides. This is especially critical for the business users that access the business meta data. Second, as with the business users the IT (information technology) staff must be willing to change the way that they build their systems in order for technical meta data to achieve a positive ROI.
In the following sections we will walk through six business and technical meta data ROI formulas. Examples of how meta data is used to accomplish these formulas were discussed in my previous two DM Review columns (September and October)1. To use these formulas you will need to know your company’s corporate revenues, cost of data warehousing, total IT budget, and the projected cost of your meta data repository project. For the examples discussed in this article I will use the values shown in Table 1.

Table 1: Sample Values
Business Meta Data ROI Formulas
There will be three business meta data ROI formulas that we will examine. Each of these business meta data ROI methods is summarized in Table 2.
The first is “Business Meta Data for the Data Warehouse” (listed in the September column as “Meta Data Driven Business User Interface”). This technique integrates business entity/attribute definitions into data warehouse/data mart reports, and business meta data report names and definitions. This improves the accuracy of our business users decision making, reduces training costs for new employees, and increases end user confidence in the IT systems.
Second is “Data Quality Tracking and Reporting”, which incorporates data quality statistics directly into data warehousing/data mart reports. These data quality statistics improve decision making in our business intelligence system and increases end user confidence in our IT systems.
The third is “Business Meta Data for Operational Systems”. Like Business Meta Data for the Data Warehouse this technique improves decision making in our operational systems, drastically reduces IT systems mistakes, improves data quality at its source, and reduces training on IT systems.
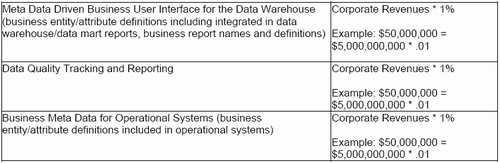
Table 2: Business Meta Data Formulas
Technical Meta Data ROI Formulas
There are three technical meta data ROI formulas that we will examine; Data Warehouse Impact Analysis, Operational Impact Analysis, and the Removal of Redundant Data/Processes. Each of these technical meta data ROI methods were presented in detail in the October 2000 DM Review column and are summarized in Table 3.
Data Warehouse Impact Analysis reduces the impact of system changes to the data warehouse environment and limits unproductive developer work. It also reduces development errors, lowers the impact of IT staff turnover and speeds up the time-to-market for new data warehouse enhancements.
Operational Impact Analysis reduces the IT impact of new systems development and changes to existing IT systems. Operational Impact Analysis limits unproductive work, reduces errors, lowers the impact of staff turnover, and speeds up the time-to-market for new IT systems.
Once a meta data repository is properly built it enables a corporation to easily identify redundant data and system processes. This is a critical issue that gets much less exposure than is properly warranted. It is important to understand that some data redundancy is appropriate, however it has been my experience that most companies needlessly store each data field redundantly four times. Companies that are
proactive in using their technical meta data to remove this redundancy can save well more than my estimate of15% of their IT budget.

Table 3: Technical Meta Data Formulas
As always I’m very interested in hearing feedback from our readers. Please feel free to send me your comments on this article at my email address below. If you want to be interactively walked through meta data ROI worksheet go to www.EWSolutions.com/book.asp. Now go forth and build your meta data repository, just remember that anything worthwhile will not be easy and that is certainly the case in building a meta data repository. Work hard and be disciplined in your development efforts and you can achieve great results.
1 Much more detail on this topic is provided in the book “Building and Managing the Meta Data Repository”, Chapter 1 Introducing Meta Data and Its Return on Investment, Marco, David. John Wiley & Sons